eta.lf
Classes for representing and modifying logical forms and eventualities.
TODO: short writeup
Module attributes
a list of special keywords that are reserved for operators in ULF. |
|
a subset of keywords that don't mirror natural language words/punctuation. |
Functions
Check whether a given wff is a conjunction predicate. |
|
Check whether a given wff is a characterization predicate. |
|
Check whether a given wff is an equality predicate. |
|
Check whether eventuality e is an expectation or intention. |
|
Extract a list of items from a wff of form |
|
Recursively read all LISP files in a given dir or list of dirs, returning a list of eventualities. |
|
Read a list of eventualities from a LISP file, modifying the list in-place. |
|
Check whether a given S-expression is a set wff. |
|
Create a set wff from a list of items. |
|
Check whether a given wff is a negative predicate. |
|
Check whether a given wff is a disjunction predicate. |
|
Parse an S-expression containing conditional keywords into a Condition eventuality. |
|
Parse an S-expression into an eventuality. |
|
Parse a list of alternating episode symbols and formulas into a list of eventualities. |
|
Parse an S-expression containing repetition keywords into a Repetition eventuality. |
|
Remove the type suffix from a ULF atom. |
|
Forms a union set wff from two set wffs. |
Classes
A Condition is a special type of Eventuality that represents a conditional event. |
|
Defines a domain of individuals. |
|
Defines an ELF formula. |
|
Defines an "eventuality", which represents an event or fact at several levels (natural language, ULF, and ELF). |
|
Defines an individual, with some canonical name and a list of aliases. |
|
Defines an abstract logical form. |
|
A Repetition is a special type of Eventuality that represents a repeating event. |
|
Defines a ULF formula. |
|
Defines a variable, with some variable symbol and some value assignment. |
- KEYWORDS = ['not', 'plur', 'past', 'pres', 'perf', 'prog', 'pasv', 'k', 'ka', 'ke', 'to', 'that', 'tht', 'fquan', 'nquan', 'nmod', 'amod', '*h', '*s', '*p', 'set-of', 'n+preds', 'np+preds', 'sub', 'rep', "'s", 'poss-by', 'adv-a', 'adv-e', 'adv-f', 'adv-s', '?', '!', '=', 'voc', 'voc-O', 'ds', 'ans-to', 'pu', 'cf', 'mod-a', 'mod-n', 'most-n', 'poss-ques', 'poss-ans']
a list of special keywords that are reserved for operators in ULF.
- KEYWORDS_R = ['plur', 'past', 'pres', 'perf', 'prog', 'pasv', 'k', 'ka', 'ke', 'to', 'tht', 'fquan', 'nquan', 'nmod', 'amod', '*h', '*s', '*p', 'set-of', 'n+preds', 'np+preds', 'sub', 'rep', 'poss-by', 'adv-a', 'adv-e', 'adv-f', 'adv-s', '=', 'voc', 'voc-O', 'ds', 'ans-to', 'pu', 'cf', 'mod-a', 'mod-n', 'most-n', 'poss-ques', 'poss-ans']
a subset of keywords that don’t mirror natural language words/punctuation.
- class Domain(individuals=[])[source]
Bases:
objectDefines a domain of individuals.
- Parameters:
individuals (list[Individual], optional) – A list of initial individuals to add to the domain.
Notes
TODO: currently incomplete and unused.
- class Individual(name, aliases=[])[source]
Bases:
objectDefines an individual, with some canonical name and a list of aliases.
- Parameters:
Notes
TODO: currently incomplete and unused.
- class Var(var, val=None)[source]
Bases:
objectDefines a variable, with some variable symbol and some value assignment.
- Parameters:
Notes
TODO: currently incomplete and unused.
- class LF(formula)[source]
Bases:
objectDefines an abstract logical form.
A logical form (whether ULF or ELF) must contain a formula, variable bindings, functions for binding/unbinding variables, for replacing variables, and for getting the formula (or a natural language representation thereof) after making all variable assignments.
- Parameters:
formula (str or s-expr) – The formula for this logical form (an S-expression or LISP-formatted string representation thereof).
- formula
The formula for this logical form.
- Type:
s-expr
- class ULF(formula)[source]
Bases:
LFDefines a ULF formula.
- Parameters:
formula (str or s-expr) – The formula for this logical form (an S-expression or LISP-formatted string representation thereof).
- class ELF(formula)[source]
Bases:
LFDefines an ELF formula.
- Parameters:
formula (str or s-expr) – The formula for this logical form (an S-expression or LISP-formatted string representation thereof).
- class Eventuality(ep, nl, ulf, elf, prob=1.0)[source]
Bases:
objectDefines an “eventuality”, which represents an event or fact at several levels (natural language, ULF, and ELF).
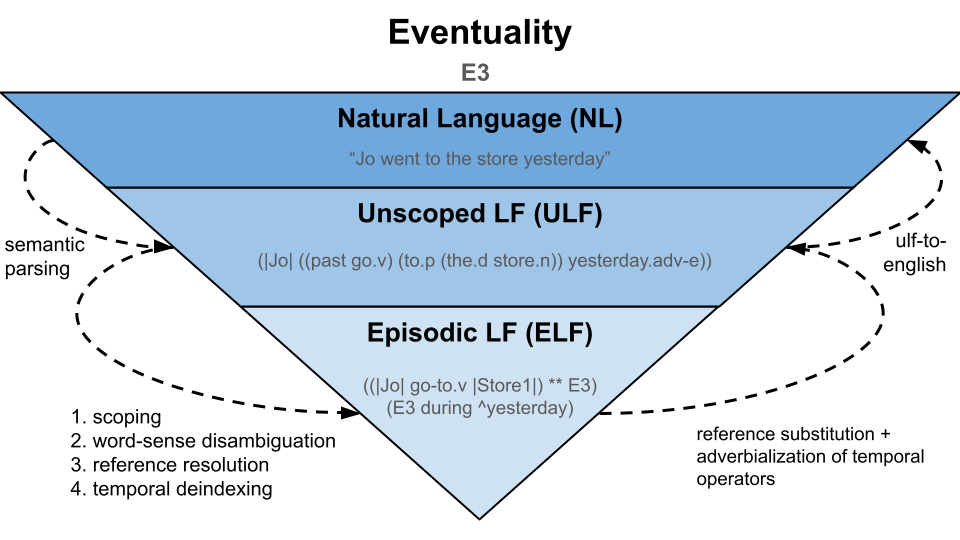
An Eventuality subsumes logical forms as well as their natural language expression, encapsulating them in one object. Minimally, an Eventuality has an episode variable/constant and a natural language string expressing the formula characterizing that event. On top of that, a ULF representation of that formula may be provided. At the highest level, a fully deindexed ELF representation may be provided.
We assume that the level of representation builds upward, i.e., a natural language string may be easily derived from the ULF, and likewise, a ULF may be easily derived from the full ELF. On the other hand, mapping from natural language to ULF requires semantic parsing, and mapping from ULF to ELF requires disambiguation, scoping, and deindexing. Hence, we want to regard those upper levels of representation as “optional”, since they may not be needed in simpler dialogue applications.
- Parameters:
ep (str) – A symbol denoting the episode variable or constant.
nl (str) – The natural language representation of the formula characterizing the event.
ulf (ULF, optional) – The ULF formula characterizing the event.
elf (ELF, optional) – The ELF formula characterizing the event.
prob (float, default=1.) – The probability associated with this event.
- replacevar(var1, var2)[source]
Replace the first variable symbol with the second variable symbol throughout the eventuality.
- embed(embedder)[source]
Embed the eventuality based on the natural language representation, given an embedder object.
- get_nl()[source]
Get the natural language representation for this eventuality, applying any variable assignments.
- get_ulf()[source]
Get the ULF representation for this eventuality, applying any variable assignments.
- get_elf()[source]
Get the ELF representation for this eventuality, applying any variable assignments.
- class Condition(ep, nl, ulf, elf, conditions, prob=1.0)[source]
Bases:
EventualityA Condition is a special type of Eventuality that represents a conditional event.
In addition to the basic Eventuality attributes, it also has a list of (<condition>, <eventualities>) pairs, where <condition> is either a ULF or True (for a default condition), and <eventualities> is a list of sub-eventualities that occur if the condition is true.
Such an event is indicated by a :try-in-sequence or :if keyword in e.g. a schema.
- class Repetition(ep, nl, ulf, elf, condition, eventualities, prob=1.0)[source]
Bases:
EventualityA Repetition is a special type of Eventuality that represents a repeating event.
In addition to the basic Eventuality attributes, it also has a condition and a sub-list of eventualities. The condition is either a ULF (or True for a repetition with no termination), such that the eventualities will occur until the condition is no longer true.
Such an event is indicated by a :repeat-until keyword in a schema.
- eventualities
The list of eventualities to repeat.
- Type:
- parse_eventuality(s, ep=None, expectation=False, prob_dict={})[source]
Parse an S-expression into an eventuality.
- Parameters:
s (s-expr) – An S-expression to parse. If s contains a condition or repetition keyword as the first element, a Condition or Repetition object is created respectively; otherwise, a basic Eventuality object is created containing s as a formula.
ep (str, optional) – If given, use this episode symbol for the created eventuality, rather than generating a new symbol.
expectation (bool, default=False) – If True, this will interpret the eventuality as an expected episode rather than an observed episode, i.e., ep will become an episode variable instead of an episode constant.
prob_dict (dict, optional) – A dictionary mapping episode symbols to probabilities, used to set the probability of this eventuality.
- Returns:
The eventuality generated according to the above parameters.
- Return type:
- parse_condition(s, ulf, ep, prob, prob_dict={})[source]
Parse an S-expression containing conditional keywords into a Condition eventuality.
- parse_repetition(s, ulf, ep, prob, prob_dict={})[source]
Parse an S-expression containing repetition keywords into a Repetition eventuality.
- parse_eventuality_list(lst, prob_dict={})[source]
Parse a list of alternating episode symbols and formulas into a list of eventualities.
- Parameters:
- Return type:
- from_lisp_file(fname, eventualities)[source]
Read a list of eventualities from a LISP file, modifying the list in-place.
- Parameters:
fname (str) – The LISP file to read.
eventualities (list[Eventuality]) – The list of eventualities to modify in-place.
- from_lisp_dirs(dirs)[source]
Recursively read all LISP files in a given dir or list of dirs, returning a list of eventualities.
- expectation_p(e)[source]
Check whether eventuality e is an expectation or intention.
An eventuality is an expectation iff it is not a special eventuality type, and the subject of its wff is not Eta.